aShell APK v0.12 (APP Android) Download Latest Version For Android
Advertisement
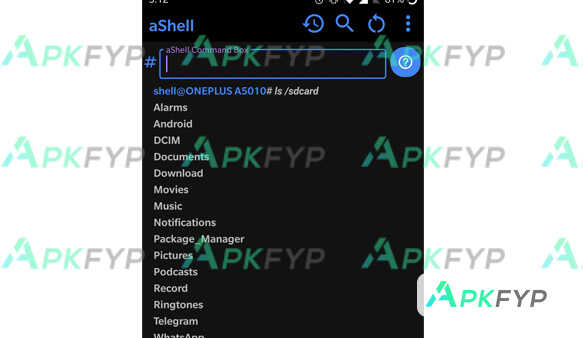
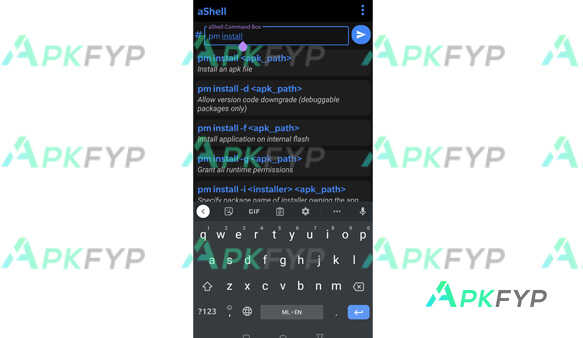
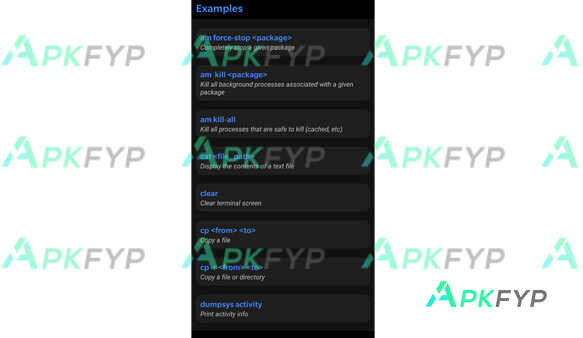
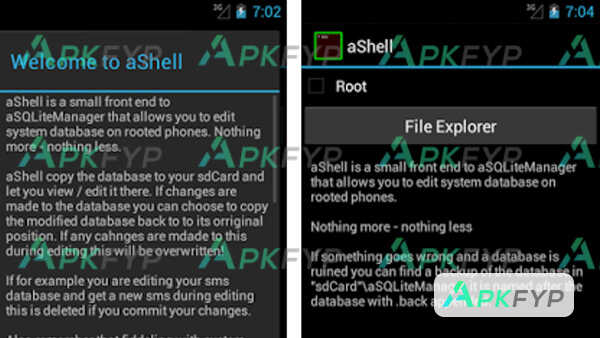
aShell APK is a versatile terminal emulator for Android devices that allows users to access a command-line interface CLI environment similar to Linux or Unix systems. It provides a powerful set of tools to run shell commands, scripts, and perform various file operations directly on Android. Unlike many other terminal applications, it supports many commands and utilities such as ls, cd, cp, mv, and even provides file management functionality and runs complex shell scripts without root access. Download it for free today and experience this popular advanced application on Apkfyp.com!